The process of creating and testing a model of a real system in order to comprehend it or close a gap is known as simulation.
Many design possibilities, including text, test, animation, voiceover, and practice-practice, can be implemented using simulations within the fundamental design forms. They facilitate experiential learning…
Modeling used in educational simulations allows for interactive learning about a particular event or activity.

Simulation is the process of simulating an actual or hypothetical dynamic system and tracking how it behaves over time. An analysis of any system’s behavior and the influence of various factors on its operating state are the goals of a simulation research. Model creation and experiments are two phases used in simulation studies. Model design is the process of creating a model that encompasses all of the critical system states. The experimentation phase starts once a reliable model has been constructed. Simulation frequently enables testing of expensive, difficult-to-implement, or unavailable systems.
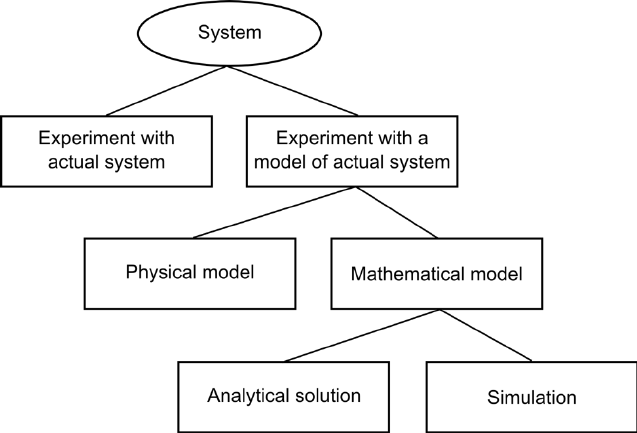
General Features of Simulation
The chance number is derived from the uniform U(0,1) distribution with a range of 0 to 1.
Using a known probability distribution to derive chance values,
starting the simulation’s timer,
Setting up the control system during the switch to the relevant simulation blocks,
Record insertion and deletion from the simulation list,
Utilizing the right data analysis techniques,
Printing the outcomes
Monitoring errors,
The employment of specialized simulation languages in simulation is mandated by these factors, along with a few others that will be discussed later. The use of simulation techniques later increased as a result of these languages. However, there has long been debate over the benefits and drawbacks of using general-purpose programming languages vs special-purpose simulation languages to create computer-based simulation situations.

Purposes of Simulation
*Simulation can be used to investigate a complicated system’s internal structure or a specific subsystem within it.
* The effects of information, organizational, and environmental changes on the behavior of the model can be investigated using simulation,
*The development of the system under consideration benefits substantially from the information received through the construction of a simulation model,
* Information is learned about which factors are more essential and how the variables interact by altering the simulation inputs and analyzing the results.
*Simulation can be utilized to support analytical solution approach as an educational aid,
*Simulation can be used to test new ideas and regulations before implementation to see what would happen.
*Analytical conclusions can be tested via simulation.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Simulation
*Difficulties in developing mathematical models by meticulously analyzing intricate real-world systems.
*Simulation; It offers a projection of system performance under these novel circumstances, enabling testing of novel regulations, parameters, or operational circumstances.
* Allows for side-by-side comparison of several designs.
* The actual system is tested without being altered, tampered with, or compromised.
*Various timelines can be used to consider the investigated system. For instance, accelerating the operation in a condensed time can be used to gather both general information about the system and specific information about the system in a broad time range.
Despite these benefits, it is also necessary to identify some downsides of simulation studies:
Also read our other Articles

